iRefScape 0.7
Date : FEB 27nd, 2010 The iRefIndex plugin for Cytoscape has not been officially released. If you are looking at this page, you have probably been directed here from the Cytoscape plugin directory at ftp://ftp.no.embnet.org/irefindex/Cytoscape/plugin . This plugin is for testing purposes only. Join the Google groups e-mail list at http://groups.google.com/group/irefindex?hl=en to be informed of the official release and updates.
Contents
- 1 Installation
- 2 Using the Wizard - an example search
- 3 Using the Search Panel
- 4 Viewing the Results
- 5 Attributes
- 6 Extra features
- 7 How to load batch query from file
- 8 Integrate user data to the plugin
- 9 Updating
- 10 Log files, search details and errors
- 11 Using the plugin as a search tool
- 12 Exit plugin and force terminate operations
- 13 Trouble shooting tips
Installation
The plugin can be installed using Cytoscape's plugin menu. Select "Manage plugins" and then "Available for Install" and then "Network and Attribute I/O" and finally "iRefIndex". Follow the on screen instructions.
More detailed instructions, trouble-shooting tips and alternative methods are available on the iRefIndex Cytoscape Plugin 0.7 installation page.
After, installation, select iRefIndex_0.7x from Cytoscape's plugin menu.
When the plugin is started for the first time, it will the publicly available dataset.
Using the Wizard - an example search
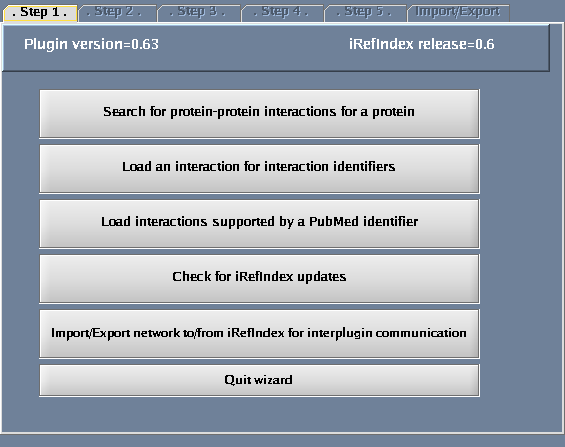
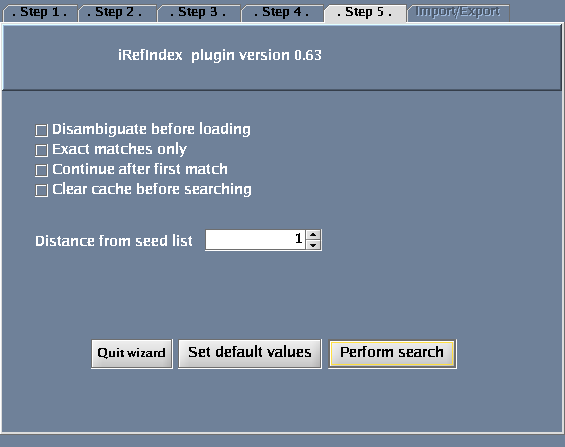
Click the "Wizard" button - a pop-up window will appear.
Follow these steps
- Select "Search protein-protein interactions for a protein".
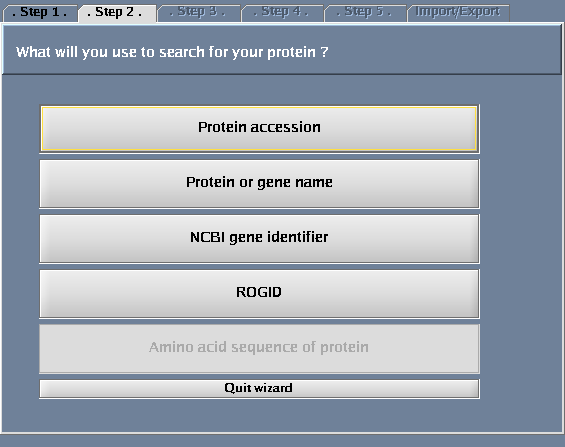
- Select "Protein or gene name".
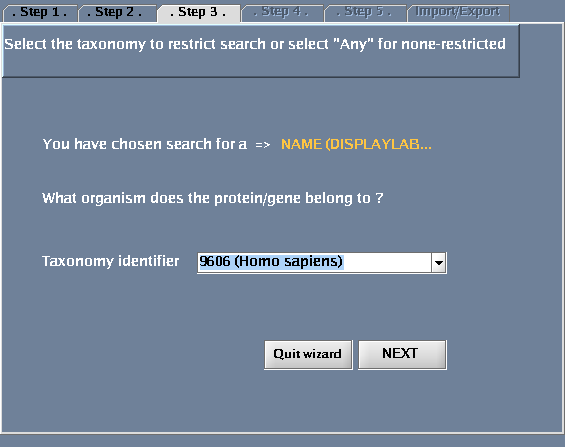
- For "Taxonomy identifier", select "9606 (Human)"
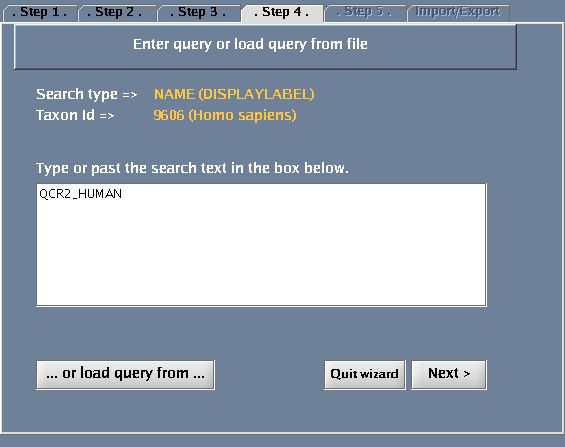
- Type QCR2_HUMAN in the provided space. Click "Next".
- Click "Perform search".
The images below show each of the steps in the wizard.
Using the Search Panel
Enter query term(s)
Queries may be loaded from a file or by pasting the query into the text-box (one query per line).
Select a Search Type.
Example searches are listed below.
| Search Type | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| RefSeq_Ac | NP_996224 | See http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/221379660 |
| UniProt_Ac | Q7KSF4 | See http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q7KSF4 |
| UniProt_ID | Q7KSF4_DROME | See http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q7KSF4 |
| geneID | 42066 | See http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=full_report&list_uids=42066 |
| geneSymbol | cher | See http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=full_report&list_uids=42066 |
| mw | 72854<-->72866 | Search protein interactors for a range of molecular weights. |
| rog | 10121899 | Redundant object group: iRefIndex's internal identifier for a protein |
| PMID | 14605208 | PubMed Identifier where an interaction is described. See http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed |
| src_intxn_id | 47513 | Source interaction database identifier. |
| omim | 227650 | OMIM identifier. See http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=227650 |
| digid | 449 | Internal identifier for a group of phenotypically related diseases. See http://donaldson.uio.no/wiki/DiG:_Disease_groups |
| dig_title | fanconi | Text search for a group of phenotypically related diseases. See http://donaldson.uio.no/wiki/DiG:_Disease_groups |
Select a taxon or type in a taxon identifier.
This will limit the search results to this organism. See http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/taxonomy for more details on taxon identifiers. In most search types, it is ok to leave this set to "Any".
Choose a distance from the query list
Selecting 0 will return only interactions between nodes found by the query list.
Selecting 1 will return immediate neighbours of nodes in the query list.
Expanded search
Selecting the "Expand result using canonical mappings" will expand the search to include all proteins that are related to the query protein (for example, splice isoforms). [See http://irefindex.uio.no/wiki/Canonicalization Canonicalization] for technical details.
Press the "Search and load" button.
Viewing the Results
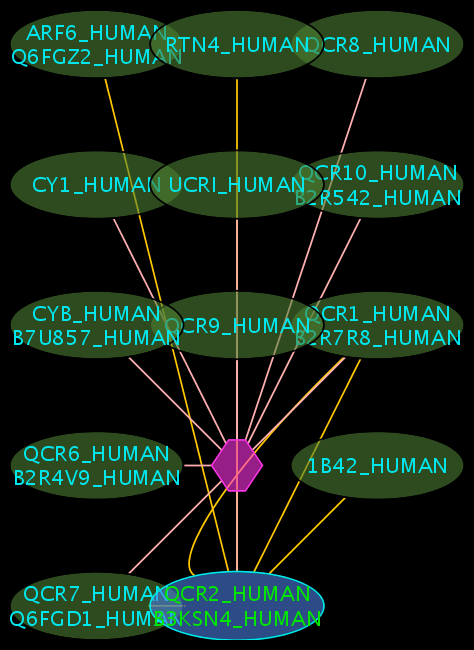
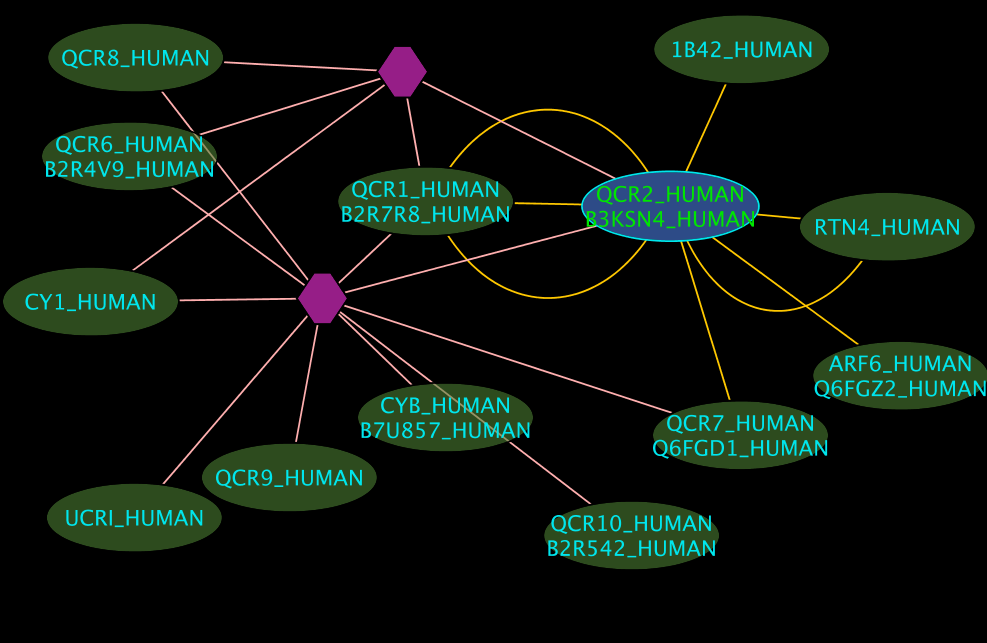
Colours and shapes
- The blue node(s) corresponds to the protein found by your query.
- Green nodes are interacting partners for your query protein.
- Purple hexagons are complex-nodes (also called pseudo-nodes). They keep partners of a complex together (i.e. QCR6_HUMAN is found in two complexes also involving “QCR2_HUMAN”).
- Orange-yellow edges indicate protein-protein interactions and pink edges represent membership of some protein in a complex.
Toggling edges Multiple edges may appear between two nodes. These represent separate interaction records that support this link. Details on each original record can be viewed using the edge attribute viewer (below). You can toggle this multi-view on and off by selecting "Toggle selected edges" in the iRefIndex menu. Only one of the edges will be shown in the collapsed view.
Expanding your interaction map
You can search for additional interactions by right-clicking on a node and selecting "Retrieve interactions" from the iRefIndex menu.
Some example result displays are shown below.
Attributes
There are two types of attributes available from iRefIndex: node attributes and edge attributes. These may be used to view information about selected nodes or edges (like i.taxid). Some features may allow the user to link out to additional data sources through the "right-click" menu (like i.geneID). Features may also be used to sort and select nodes and edges with specific attributes (like i.order). The i.query feature shows the user's query that is responsible for returning the node or edge.
Brief descriptions and examples of each attribute are provided below.
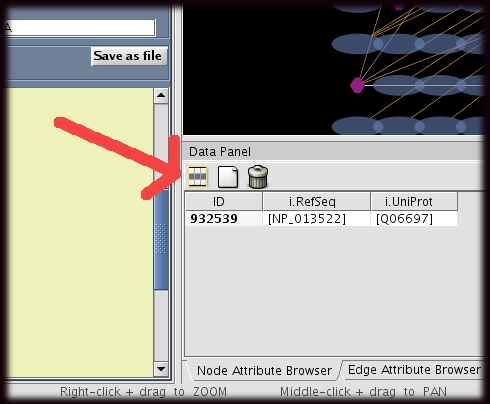
- The user must first select the attributes that are to be displayed.
- This can be done by clicking on the "attribute" icon at the top of the node or edge attribute browser (red arrow).
Node Attributes
Each node represents a distinct amino acid sequence (protein) from a distinct organism (taxon id). Each of the attributes below, provide additional information about the node. Although each node is distinct, a graph produced by iRefIndex may contain multiple nodes that are related proteins (i.e., splice isoform products from the same gene). These nodes will all have the same "i.canonical_rog" and i.canonical_rogid" feature values. See notes below.
Node attributes that can be lists of items (like i.UniProt) will have a corresponding attribute called i.[attribute name]_TOP (e.g. i.UniProt_TOP) that is the first item of the list.
| Attribute name | Data type | Example value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | 10121899 | This is a unique identifier for the node assigned by iRefIndex (no two nodes will have the same ID). Each node corresponds to distinct amino acid sequence from a distinct taxon id. See also i.rog and i.rogid |
| canonicalName | Integer | 10121899 | This is the same as ID. This attribute is set by Cytoscape and is unrelated to the i.canonical_rog or i.canonical_rogid used by iRefIndex |
| i.RefSeq_Ac | List | [NP_996224] | All RefSeq accessions with an amino acid sequence and taxon identifier identical to the protein represented by this node. Right click on this entry and select "Search [RefSeq_Ac] on the web -- Entrez -- Protein" for more information. See also i.RefSeq_TOP for the first entry in this list of accessions. |
| i.UniProt_Ac | List | [Q7KSF4] | All UniProt accessions with an amino acid sequence and taxon identifier identical to the protein represented by this node. Right click on this entry and select "Search [UniProt_Ac] on the web -- UniProt -- KB Beta" for more information. See also i.UniProt_Ac_TOP for the first entry in this list of accessions. |
| i.UniProt_ID | List | [Q7KSF4_DROME] | All UniProt IDs with an amino acid sequence and taxon identifier identical to the protein represented by this node. Right click on this entry and select "Search [UniProt_ID] on the web -- UniProt -- KB Beta" for more information. See also i.UniProt_ID_TOP for the first entry in this list of IDs. |
| i.canonical_rog | Integer | 10121899 | Related proteins (say splice isoforms from the same gene) will all belong to the same canonical group. One member of this group is assigned as the canonical representative of this group. The i.canonical_rog attribute lists the identifier of the protein's canonical group identifier. For example, all products of Entrez Gene 42066 have the same i.canonical_rog (10121899). Each of these gene products has its own identifier (because they each have a distinct amino acid sequence). One of the splice isoforms (NP_996224) was chosen as the canonical representative of this group. See http://irefindex.uio.no/wiki/Canonicalization for more details on how canonical groups are constructed and how canonical representatives are chosen. |
| i.canonical_rogid | String | 1ZFb1WlW0OgOlhiAPtkJTdb6oOg7227 | This is a unique alphanumeric key for the canonical representative of the canonical group to which this node belongs. Briefly, an SHA-1 digest of the amino acid sequence is used to generate a unique 27 character key and this is pre-pended to the taxon id for the protein's source organism in order to make the rogid. See PMID 18823568 for details on how this key can be generated. This is a string equivalent of the i.canonical_rog attribute. All canonical_rog's (an integer) have one corresponding canonical_rogid. See http://irefindex.uio.no/wiki/Canonicalization for more details on how canonical groups are constructed and how canonical representatives are chosen. Note that the rogid for the protein represented by this specific node is listed under i.rogid. |
| i.dataset | Integer | 0 | TO BE DESCRIBED |
| i.digid | List | 449 | This is an integer identifier that is shared by a group of disease entries in OMIM that are related by their titles. See http://donaldson.uio.no/wiki/DiG:_Disease_groups for more details. Also see i.omim and i.dig_title. |
| i.dig_title | List | [Fanconi anemia, complementation group B, 300514 (3), VACTERL association with hydrocephalus, X-linked, 314390 (3)] | These are entries from OMIM's Morbid Map that are all part of the same disease group. See http://donaldson.uio.no/wiki/DiG:_Disease_groups for more details. Also see i.omim and i.digid. |
| i.displayLabel | List | [Q7KSF4_DROME] | This is a list of short labels chosen by iRefIndex to label the node using the VizMapper. The UniProt ID is preferentially chosen (if one is available) followed by the Entrez Gene Symbol. See also i.displayLabel_TOP for the first entry in this list. |
| i.geneID | List | [42066] | All NCBI Entrez Gene Identifiers that encode a protein sequence identical to that of this node. Right click on this entry and select "Search [geneID] on the web -- Entrez -- Gene" for more information. See also i.geneID_TOP for the first entry in this list. |
| i.geneSymbol | List | [CHER] | All NCBI Entrez Gene Official Sybols that encode a protein sequence identical to that of this node. Right click on this entry and select "Search [geneSymbol] on the web -- Entrez -- Gene" for more information. See also i.geneSymbol_TOP for the first entry in this list. |
| i.interactor_description | List | [Q7KSF4_DROME, CHER, DMEL_CG3937, SKO, DMEL CG3937, FLN, CG3937, CHER, DMEL\\CG3937, FLN, SKO, CHER, NAME=CHER, DMEL_CG3937] | A collection of all the names in their short form as given by the original interaction databases. See also i.interactor_description_TOP for the first entry in this list. |
| i.mw | Integer | 259142 | Molecular weight associated with the protein sequence for this node. From UniProt if available. You can search for nodes inside a MW range using the "mw" search type in the iRefIndex plugin. |
| i.omim | List | [608053] | List of OMIM disease identifiers associated with this protein. Right click on the entry ans select Search for [omim] on the web -- Entrez -- OMIM for more information. |
| i.order | Integer | 0 | TO BE DESCRIBED. The distance of this node from the query node (query node = 0 , direct neighbors = 1 ). Pseudonodes have negative values (-1 = complex holder, -2 = collapsed instance ) |
| i.overall_degree | Integer | 42 | The total number of interactions described for this node in the iRefIndex database. Not all of these edges will be necessarily shown in the current view. |
| i.popularity | List | 42 | TO BE DESCRIBED |
| i.pseudonode | Boolean | false | This is set to true is the node represents a "complex" or n-ary interaction record. Protein nodes with edges incident to a pseudonode are member interactors from the interaction record where specific interactions between pairs of interactors is unknown. Pseudonodes appear as hexagons when using the iRefIndex VizMapper style. |
| i.query | String | NP_996224 | The user query used to retrieve this specific node. Neighbours of "query" nodes will not have an i.query value. Nodes returned by queries are coloured blue when using the iRefIndex VizMapper style. |
| i.rog | Integer | 10121899 | This is a unique identifier for the node assigned by iRefIndex (no two nodes will have the same ID). Each node corresponds to distinct amino acid sequence from a distinct taxon id. i.rog also appears as the ID attribute. Each i.rog has a corresponding i.rogid - see below. |
| i.rogid | String | 2mL9oLZ9g/SSPyK0nOz97RmOzPg3702 | This is a unique alphanumeric key for the protein represented by this node. Briefly, an SHA-1 digest of the amino acid sequence is used to generate a unique 27 character key and this is pre-pended to the taxon id for the protein's source organism in order to make the rogid. See PMID 18823568 for details on how this key can be generated. This is a string equivalent of the i.rog attribute. All i.rog's (an integer) have one corresponding i.rogid. |
| i.taxid | Integer | 7227 | The NCBI taxonomy identifier for this protein's source organism. See http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/taxonomy?term=7227 for more details. |
| i.xref | List | [AAF70826.1,Q9M6R5] | All the accessions as given by the original interaction database records to describe this protein. See also i.xref_TOP for the first entry in this list. |
Edge Attributes
Each edge represents a distinct primary database record that supports some relationship between the two incident nodes. So, if an interaction between two proteins has been annotated by two databases (or twice by the same database) then two edges will appear between those two protein nodes.
| Attribute name | Data type | Example value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | String | 10121899 (2771704(40952)) 13911416 | This is a unique identifier for the edge assigned by Cytoscape (no two edges would have same ID). See i.rig and i.rigid for unique identifiers for the edge assigned by iRefIndex. |
| i.PMID | Integer | 14605208 | Publication identifier of the publication where the interaction represented by the edge mentioned. Right click on this entry and select: Search [PMID] on the web -- Entrez -- Pubmed for more details on the publication. |
| i.bait | Integer | 13911416 | Node ID for the protein that was used as a bait in this experiment. Only applicable where the experimental system (see i.method_name) used to support this relationship was a bait-prey system (e.g. two hybrid). |
| i.canonical_rig | Integer | 27799 | See notes for i.rig edge feature. This is the rig constructed for the interaction using its canonical rogs. Use a web browser to query http://wodaklab.org/iRefWeb/interaction/show/27799 (where 27799 is the canonical_rig) to retrieve more information on this interaction and equivalent source interaction records. |
| i.experiment | String | Giot L [2003] | A short label for the experiment where this interaction was found (usually contains authors names). |
| i.flag | Integer | 1 | Used by iRefIndex plugin to control display of edges (0- the representative edge, used in edge toggle, 1- an edge which will disappear during edge toggle, 2- complex holder edge,6-a path, 7-Edge from or to a collapsed node). |
| i.host_taxid | Integer | 7227 | Indicates the organism taxon id where the interaction was experimentally demonstrated. |
| i.isLoop | Integer | 1 | Indicates whether the interaction is a self interaction (i.e dimer or possibly multimer of the same protein type). See the source interaction record for details. |
| i.method_cv | String | MI:0018 | PSI-MI controlled vocabulary term id for the method used to provide evidence for this interaction. See http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ontology-lookup/ for more details. The name of the method is also given in the i.method_name feature. |
| i.method_name | String | two hybrid | PSI-MI controlled vocabulary term name for the method used to provide evidence for this interaction. See http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ontology-lookup/ for more details. The term identifer is also given in the i.method_cv feature. |
| i.participant_identification | String | predetermined participant | PSI-MI controlled vocabulary term for the participant identification method used to provide evidence for this interaction. See http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ontology-lookup/ for more details. The identifier for the term is also given in the i.participant_cv feature. |
| i.participant_cv | String | predetermined participant | PSI-MI controlled vocabulary term id for the participant identification method used to provide evidence for this interaction. See http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ontology-lookup/ for more details. The term itself is also given in the i.participant_identification feature. |
| i.type_cv | String | MI:0407 | PSI-MI controlled vocabulary term id for the interaction type that occurs between the two proteins. See http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ontology-lookup/ for more details. The term itself is also given in the i.type_name feature. |
| i.type_name | String | direct interaction | PSI-MI controlled vocabulary term id for the interaction type that occurs between the two proteins. See http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ontology-lookup/ for more details. The term itself is also given in the i.type_name feature. |
| i.query | String | NP_996224 | The user's query that is responsible for returning this edge. |
| i.rig | Integer | 27799 | Redundant interaction group identifier for the interaction. This is an integer equivalent of the i.rigid. Every rig has one corresponding rigid. |
| i.rigid | String | TAabV6yJ1XzUvEhYwZLpu5reBU0 | Redundant interaction group identifier for the interaction. This is a universal key generated for the interaction by asciibetically ordering and concatentating the rogids participating in the interaction and then generating a Base-64 representation of an SHA-1 digest of the resulting string. See PMID 18823568 for details on how this key can be generated. |
| i.score_hpr | Integer | 15 | The hpr score (highest pmid re-use) is the highest number of interactions that any one PMID (supporting this interaction) is used to support. See PMID 18823568 for details. See also score_np and score_lpr. |
| i.score_lpr | Integer | 11 | The lpr score (lowest pmid re-use) is the lowest number of distinct interactions that any one PMID (supporting this interaction) is used to support. An lpr of greater than 20 is considered to be a high-throughput experiment. See PMID 18823568 for details. See also score_np and score_lpr. |
| i.np | Integer | 2 | Number of PubMed Identifiers (PMIDs) pointing to literature where this interaction is supported. See PMID 18823568 for details. See also score_np and score_lpr. |
| i.source_protein | Integer | -1 | TO BE DESCRIBED |
| i.src_intxn_db | String | grid | Original interaction database where this interaction record was obtained. |
| i.src_intxn_id | String | 38677 | Original interaction database where this interaction record was obtained.
In some case, it may be possible to right click and Search [src_intxn_id] on the web -- Interaction databases -- the database to see the original record. |
| i.target_protein | Integer | -1 | TO BE DESCRIBED |
Extra features
To be described
- Edge Toggle
- Load user variables
How to load batch query from file
1. Create a text file with the following format:
<type><NCBI_taxonomy_identifier>
query_text_1
query_text_2
query_text_3
The first line of the file starts with a hash ("#") and then the type. The type could be
- ACCESSION
- NAME
- GENID
The query_text is your query (e.g.Q39009). Each query line has to be terminated by a new line character (press enter after each line)
[Sample batch file: [1]]
Integrate user data to the plugin
How to create your own file to use as index
How to create node and edge attributes
Example: Attaching disease group identifiers to Nodes (http://irefindex.uio.no/wiki/DiG:_Disease_groups)
Updating
- From Cytoscape updater
- Using plugins update feature
Log files, search details and errors
- How to interpret log messages and save them for later reference.
Using the plugin as a search tool
The plugin could also be used to search the current network. However, there is a better search option in Cytoscape with Google suggest which may be more convenient to use. The reason for including the search function was that the Cytoscape search filed remained inactive on some occasions for networks crated using the plugin. The reason for this is still unknown and deleting a node on the network seems to activate it, when this bug will be fixed the users are encouraged to use the Cytoscape search option. Currently, if a user performs a search with a term and if the corresponding protein is already loaded, the loaded protein (corresponding node) would be highlighted with Cytoscape default highlight colors.
Exit plugin and force terminate operations
The exit button performs two functions.
- First one is to exit iRefIndex plugin, where the outcome is to detach the plugin from Cytoscape.
- The second function "FORCE STOP" (only available during a active task) is to terminate current operation. The "FORCE STOP" is useful when the search query or a subsequent operation takes too long to finish or none-responding. When a force stop is performed the out come is unpredictable and behavior was undefined, therefore results after such operation could not be trusted.
Trouble shooting tips
- See http://cytoscape.org for a manual and a set of tutorials which describe the installation and use of Cytoscape.
- For problems with Cytoscape installation or use, try the Cytoscape Help Desk
- If you have problems with installation or use, please share your experience with us through the iRefIndex Google Group
- When updating data on Microsoft Windows XP and Vista. "Failed to find resources message" may appear in the log message window. If this happens please run the update again and the plugin will check and correct the problem during the second attempt.
- If you are working with large graphs, make sure Cytoscape has at least 128MB memory. See the following document for more information on setting up memory: http://cytoscape.org/cgi-bin/moin.cgi/How_to_increase_memory_for_Cytoscape